2022CUDA夏季训练营Day5实践

2022CUDA夏季训练营Day1实践 https://bbs.huaweicloud.cn/blogs/364478
2022CUDA夏季训练营Day2实践 https://bbs.huaweicloud.cn/blogs/364479
2022CUDA夏季训练营Day3实践 https://bbs.huaweicloud.cn/blogs/364480
2022CUDA夏季训练营Day4实践之统一内存 https://bbs.huaweicloud.cn/blogs/364481
2022CUDA夏季训练营Day4实践之原子操作 https://bbs.huaweicloud.cn/blogs/364482
Day4课后作业如下:

其中第一题,在上面的Day4链接中,张小白已经做了。
那么第二题怎么做呢?
老师提供了一个函数是给top k个字段排序的:
__device__ __host__ void insert_value(int* array, int k, int data)
{
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
if (array[i] == data)
{
return;
}
}
if (data < array[k - 1])
return;
for (int i = k - 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (data > array[i])
array[i + 1] = array[i];
else {
array[i + 1] = data;
return;
}
}
array[0] = data;
}我们求解top10的思路是什么呢?
当然仍然是延续这个万能的框架。
我们来看下求最大值和最小值的框架,只留下最大值的部分:
2_1.cu
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdint.h>
#include<time.h> //for time()
#include<stdlib.h> //for srand()/rand()
#include<sys/time.h> //for gettimeofday()/struct timeval
#include"error.cuh"
#define N 10000000
#define BLOCK_SIZE 256
#define BLOCKS ((N + BLOCK_SIZE - 1) / BLOCK_SIZE)
__managed__ int source[N]; //input data
__managed__ int final_result[2] = {INT_MIN,INT_MAX}; //scalar output
__global__ void _sum_min_or_max(int *input, int count,int *output)
{
__shared__ int max_per_block[BLOCK_SIZE];
int max_temp = INT_MIN;
for (int idx = threadIdx.x + blockDim.x * blockIdx.x;
idx < count;
idx += gridDim.x * blockDim.x
)
{
max_temp = (input[idx] > max_temp) ? input[idx] :max_temp;
}
max_per_block[threadIdx.x] = max_temp; //the per-thread partial max is temp!
__syncthreads();
//**********shared memory summation stage***********
for (int length = BLOCK_SIZE / 2; length >= 1; length /= 2)
{
int max_double_kill = -1;
if (threadIdx.x < length)
{
max_double_kill = (max_per_block[threadIdx.x] > max_per_block[threadIdx.x + length]) ? max_per_block[threadIdx.x] : max_per_block[threadIdx.x + length];
}
__syncthreads(); //why we need two __syncthreads() here, and,
if (threadIdx.x < length)
{
max_per_block[threadIdx.x] = max_double_kill;
}
__syncthreads(); //....here ?
} //the per-block partial sum is sum_per_block[0]
if (blockDim.x * blockIdx.x < count) //in case that our users are naughty
{
//the final reduction performed by atomicAdd()
if (threadIdx.x == 0) atomicMax(&output[0], max_per_block[0]);
}
}
int _max_min_cpu(int *ptr, int count, int *max1, int *min1)
{
int max = INT_MIN;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
max = (ptr[i] > max)? ptr[i]:max;
}
//printf(" CPU max = %d\n", max);
*max1 = max;
return 0;
}
void _init(int *ptr, int count)
{
uint32_t seed = (uint32_t)time(NULL); //make huan happy
srand(seed); //reseeding the random generator
//filling the buffer with random data
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
//ptr[i] = rand() % 100000000;
ptr[i] = rand() ;
if (i % 2 == 0) ptr[i] = 0 - ptr[i] ;
}
}
double get_time()
{
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
return ((double)tv.tv_usec * 0.000001 + tv.tv_sec);
}
int main()
{
//**********************************
fprintf(stderr, "filling the buffer with %d elements...\n", N);
_init(source, N);
//**********************************
//Now we are going to kick start your kernel.
cudaDeviceSynchronize(); //steady! ready! go!
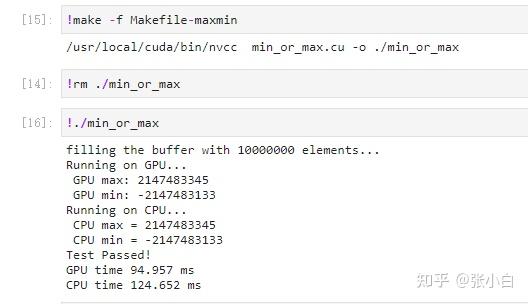
fprintf(stderr, "Running on GPU...\n");
double t0 = get_time();
_sum_min_or_max<<<BLOCKS, BLOCK_SIZE>>>(source, N,final_result);
CHECK(cudaGetLastError()); //checking for launch failures
CHECK(cudaDeviceSynchronize()); //checking for run-time failures
double t1 = get_time();
fprintf(stderr, " GPU max: %d\n", final_result[0]);
//**********************************
//Now we are going to exercise your CPU...
fprintf(stderr, "Running on CPU...\n");
double t2 = get_time();
int cpu_max=0;
int cpu_min=0;
int B = _max_min_cpu(source, N, &cpu_max, &cpu_min);
printf(" CPU max = %d\n", cpu_max);
printf(" CPU min = %d\n", cpu_min);
double t3 = get_time();
//fprintf(stderr, "CPU sum: %u\n", B);
//******The last judgement**********
//if ( final_result_max == cpu_max && final_result_min == cpu_min )
if ( final_result[0] == cpu_max )
{
fprintf(stderr, "Test Passed!\n");
}
else
{
fprintf(stderr, "Test failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
//****and some timing details*******
fprintf(stderr, "GPU time %.3f ms\n", (t1 - t0) * 1000.0);
fprintf(stderr, "CPU time %.3f ms\n", (t3 - t2) * 1000.0);
return 0;
} 编译运行:
那么,我们继续在这个框架的基础上,把计算top 10的部分加上去。
该怎么加呢?
显然的,需要把上面计算max的部分全部换成计算top10的部分:
我们看到上面两个定义:
__shared__ int max_per_block[BLOCK_SIZE];
int max_temp =0;
max_per_block是存放最大值的,现在要存放topk(k=10)个最大值,所以显然我们需要将max_per_block[BLOCK_SIZE]扩容成 max_per_block[BLOCK_SIZE* topk],
为了对比方便,将max_per_block改为 topk_per_block:
同理,将max_temp扩充为 topk_temp[topk];
第2个地方:根据 inut[idx]计算出 topk_temp:
max_temp = (input[idx] > max_temp) ? input[idx] :max_temp;直接改为
insert_value(topk_temp, TOPK, input[idx]);第3个地方:根据topk_temp 计算出 topk_per_block[ threadIdx.x * TOPK ]到 topk_per_block[ threadIdx.x * TOPK+TOPK-1 ] :
max_per_block[threadIdx.x] = max_temp; //the per-thread partial max is temp!改为:
for(int i = 0; i< TOPK ; i++)
{
topk_per_block[ threadIdx.x * TOPK + i] = topk_temp[i];
}第4个地方:
max_double_kill = (max_per_block[threadIdx.x] > max_per_block[threadIdx.x + length]) ? max_per_block[threadIdx.x] : max_per_block[threadIdx.x + length];这里原来是取 max_per_block[threadIdx.x] 和 max_per_block[threadIdx.x + length]) 间的最大值,同样换成insert_value函数:
for(int i=0;i<TOPK ;i++)
{
insert_value(topk_temp, TOPK , topk_per_block[ (threadIdx.x + length) * TOPK + i]);
}第5个地方:
max_per_block[threadIdx.x] = max_double_kill;改为:
for(int i=0;i<TOPK ;i++)
{
topk_per_block[threadIdx.x *TOPK + i]= topk_temp[i];
}第6个地方:
if (threadIdx.x == 0) atomicMax(&output[0], max_per_block[0]);改为:
for(int i=0;i<TOPK ;i++)
{
output[TOPK * blockIdx.x +i ] = topk_per_block[i];
}注:这里可以更简单的改为:
if (threadIdx.x < TOPK) output[TOPK * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x ] = topk_per_block[threadIdx.x];这样直接整体并行写入即可,而且还是合并的。
核函数改完之后,调用核函数的地方也做以下改动:
_sum_min_or_max<<<BLOCKS, BLOCK_SIZE>>>(source, N,final_result);改为
_sum_min_or_max<<<BLOCKS, BLOCK_SIZE>>>(source, N, _1pass_results);
_sum_min_or_max<<<1, BLOCK_SIZE>>>(_1pass_results, TOPK * BLOCKS, final_result);这里需要解释一下,为啥原来取最大值的时候调用一次核函数就行了,但是取TOPK就需要调用2次呢?
因为并没有一个同时处理TOPK个元素替换的原子操作(但是有很多替换1个元素的原子操作)
当然,比较CPU和GPU的地方也做相应的改动(这点看下面的代码就行了)
修改完的代码如下:
2_1.cu
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdint.h>
#include<time.h> //for time()
#include<stdlib.h> //for srand()/rand()
#include<sys/time.h> //for gettimeofday()/struct timeval
#include"error.cuh"
#define N 10000000
#define BLOCK_SIZE 256
#define BLOCKS ((N + BLOCK_SIZE - 1) / BLOCK_SIZE)
#define TOPK 10
__managed__ int source[N]; //input data
__managed__ int final_result[TOPK] = {INT_MIN}; //scalar output
__managed__ int _1pass_results[TOPK * BLOCKS];
__device__ __host__ void insert_value(int* array, int k, int data)
{
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
if (array[i] == data)
{
return;
}
}
if (data < array[k - 1])
return;
for (int i = k - 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (data > array[i])
array[i + 1] = array[i];
else {
array[i + 1] = data;
return;
}
}
array[0] = data;
}
__global__ void _sum_min_or_max(int *input, int count,int *output)
{
//__shared__ int max_per_block[BLOCK_SIZE];
__shared__ int topk_per_block[BLOCK_SIZE * TOPK];
//int max_temp = INT_MIN;
int topk_temp [TOPK];
for(int i=0;i<TOPK;i++) topk_temp[i] = INT_MIN;
for (int idx = threadIdx.x + blockDim.x * blockIdx.x;
idx < count;
idx += gridDim.x * blockDim.x
)
{
//max_temp = (input[idx] > max_temp) ? input[idx] :max_temp;
insert_value(topk_temp, TOPK, input[idx]);
}
//max_per_block[threadIdx.x] = max_temp; //the per-thread partial max is temp!
for(int i = 0; i< TOPK ; i++)
{
topk_per_block[ threadIdx.x * TOPK + i] = topk_temp[i];
}
__syncthreads();
//**********shared memory summation stage***********
for (int length = BLOCK_SIZE / 2; length >= 1; length /= 2)
{
//int max_double_kill = -1;
if (threadIdx.x < length)
{
//max_double_kill = (max_per_block[threadIdx.x] > max_per_block[threadIdx.x + length]) ? max_per_block[threadIdx.x] : max_per_block[threadIdx.x + length];
for(int i=0;i<TOPK ;i++)
{
insert_value(topk_temp, TOPK , topk_per_block[ (threadIdx.x + length) * TOPK + i]);
}
}
__syncthreads(); //why we need two __syncthreads() here, and,
if (threadIdx.x < length)
{
//max_per_block[threadIdx.x] = max_double_kill;
for(int i=0;i<TOPK ;i++)
{
topk_per_block[threadIdx.x * TOPK + i]= topk_temp[i];
}
}
__syncthreads(); //....here ?
} //the per-block partial sum is sum_per_block[0]
if (blockDim.x * blockIdx.x < count) //in case that our users are naughty
{
//the final reduction performed by atomicAdd()
// if (threadIdx.x == 0) atomicMax(&output[0], max_per_block[0]);
if (threadIdx.x < TOPK) output[TOPK * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x ] = topk_per_block[threadIdx.x];
/*
for(int i=0;i<TOPK ;i++)
{
output[TOPK * blockIdx.x +i ] = topk_per_block[i];
}
*/
}
}
int _max_min_cpu(int *ptr, int count, int *max1, int *min1)
{
int max = INT_MIN;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
max = (ptr[i] > max)? ptr[i]:max;
}
//printf(" CPU max = %d\n", max);
*max1 = max;
return 0;
}
void cpu_result_topk(int* input, int count, int* output)
{
/*for (int i = 0; i < TOPK; i++)
{
output[i] = INT_MIN;
}*/
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
insert_value(output, TOPK, input[i]);
}
}
void _init(int *ptr, int count)
{
uint32_t seed = (uint32_t)time(NULL); //make huan happy
srand(seed); //reseeding the random generator
//filling the buffer with random data
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
//ptr[i] = rand() % 100000000;
ptr[i] = rand() ;
if (i % 2 == 0) ptr[i] = 0 - ptr[i] ;
}
}
double get_time()
{
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
return ((double)tv.tv_usec * 0.000001 + tv.tv_sec);
}
int main()
{
cudaEvent_t start, stop;
CHECK(cudaEventCreate(&start));
CHECK(cudaEventCreate(&stop));
//**********************************
fprintf(stderr, "filling the buffer with %d elements...\n", N);
_init(source, N);
//**********************************
//Now we are going to kick start your kernel.
CHECK(cudaEventRecord(start));
cudaDeviceSynchronize(); //steady! ready! go!
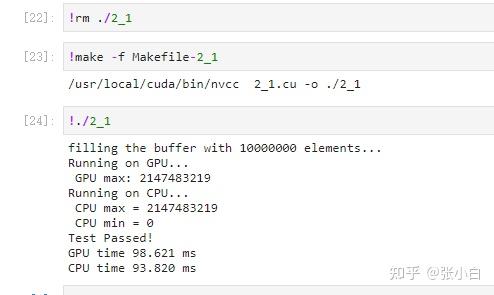
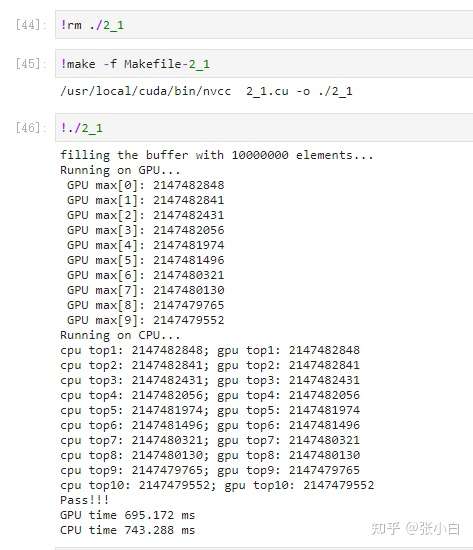
fprintf(stderr, "Running on GPU...\n");
double t0 = get_time();
// _sum_min_or_max<<<BLOCKS, BLOCK_SIZE>>>(source, N,final_result);
_sum_min_or_max<<<BLOCKS, BLOCK_SIZE>>>(source, N, _1pass_results);
CHECK(cudaGetLastError()); //checking for launch failures
_sum_min_or_max<<<1, BLOCK_SIZE>>>(_1pass_results, TOPK * BLOCKS, final_result);
CHECK(cudaGetLastError()); //checking for launch failures
CHECK(cudaDeviceSynchronize()); //checking for run-time failures
CHECK(cudaEventRecord(stop));
CHECK(cudaEventSynchronize(stop));
double t1 = get_time();
for(int i=0;i<TOPK;i++)
fprintf(stderr, " GPU max[%d]: %d\n", i,final_result[i]);
//**********************************
//Now we are going to exercise your CPU...
fprintf(stderr, "Running on CPU...\n");
double t2 = get_time();
int cpu_result[TOPK] = { 0 };
//int cpu_max=0;
//int cpu_min=0;
//int B = _max_min_cpu(source, N, &cpu_max, &cpu_min);
cpu_result_topk(source, N, cpu_result);
//printf(" CPU max = %d\n", cpu_max);
double t3 = get_time();
//fprintf(stderr, "CPU sum: %u\n", B);
int ok = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < TOPK; ++i)
{
printf("cpu top%d: %d; gpu top%d: %d \n", i + 1, cpu_result[i], i + 1, final_result[i]);
if (fabs(cpu_result[i] - final_result[i]) > (1.0e-10))
{
ok = 0;
}
}
if (ok)
{
printf("Pass!!!\n");
}
else
{
printf("Error!!!\n");
}
//******The last judgement**********
/*
//if ( final_result_max == cpu_max && final_result_min == cpu_min )
if ( final_result[0] == cpu_max )
{
fprintf(stderr, "Test Passed!\n");
}
else
{
fprintf(stderr, "Test failed!\n");
exit(-1);
}
*/
//****and some timing details*******
fprintf(stderr, "GPU time %.3f ms\n", (t1 - t0) * 1000.0);
fprintf(stderr, "CPU time %.3f ms\n", (t3 - t2) * 1000.0);
return 0;
} 我们来运行一下:
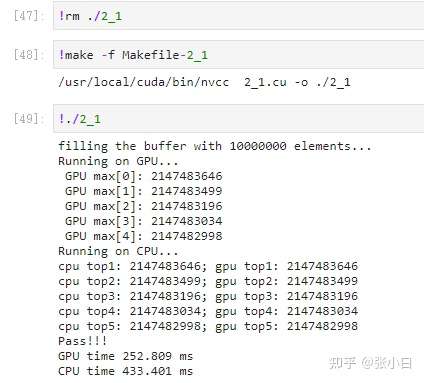
这样下去,算top5,top20,top50应该都是可以的吧?
top5:
top20:
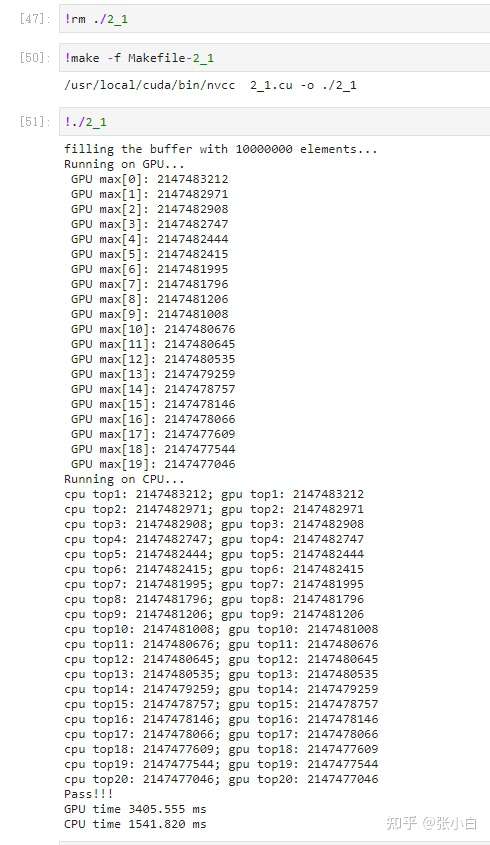
top50:
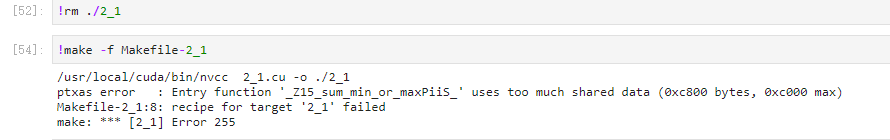
LOL,张小白想得太美好了~~
只好改为top40看看:貌似算得有点慢了,但是还能出个结果:
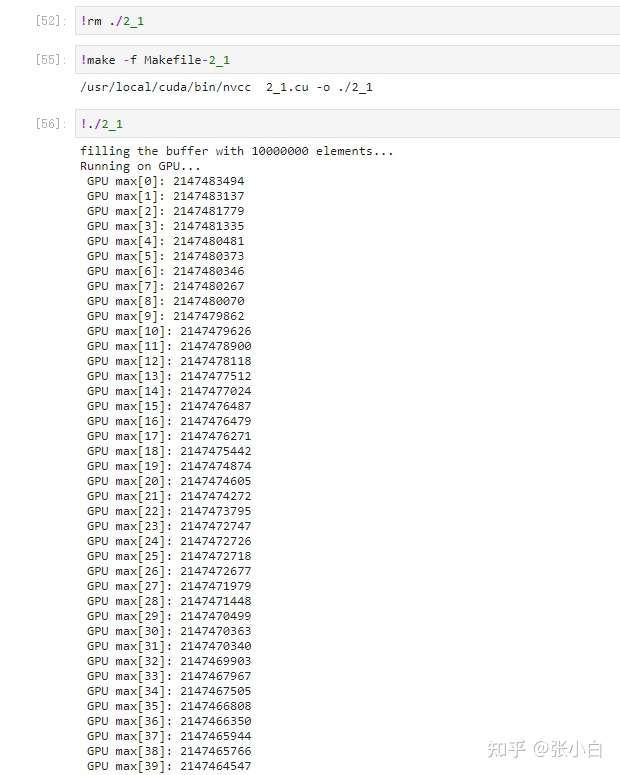

那到底有什么好的计算方式呢?
还有,现有方式还能提速吗?
这个萧敬腾的天气,又给张小白创造了好几个难题。。。。
看来还得好好学习啊。。。
另外,张小白忘记自己还有个Jetson AGX Orin了。让我们看看它能不能突破下极限:
仍然用top40计算。
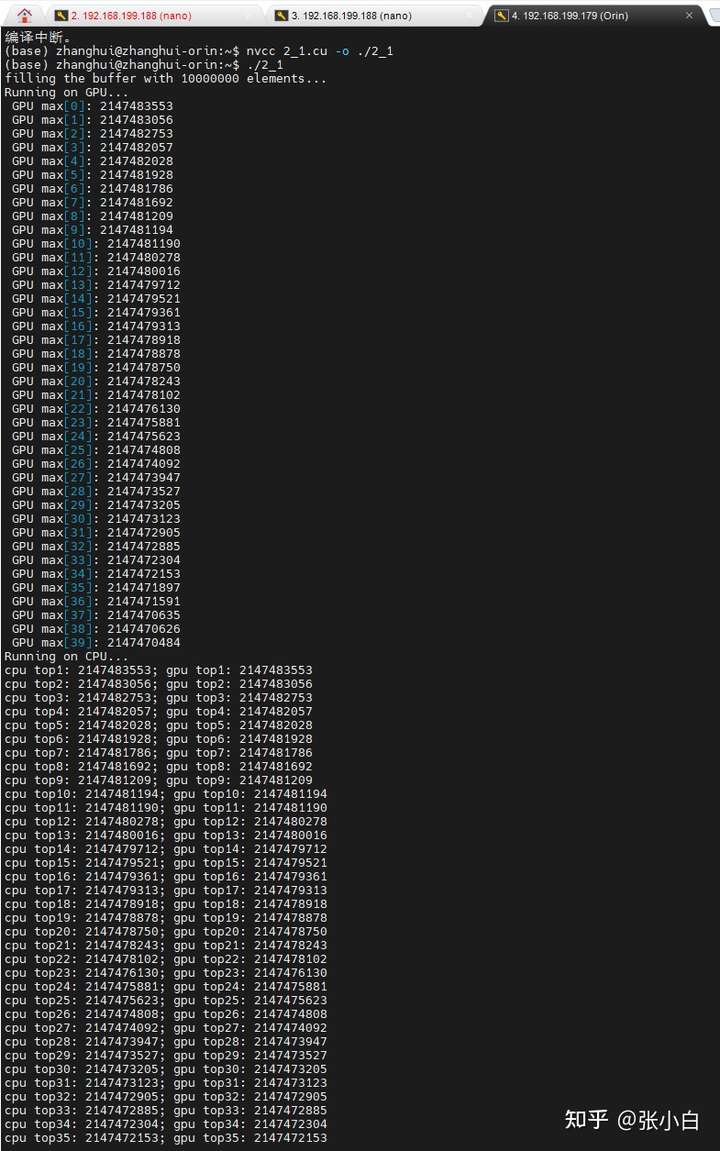
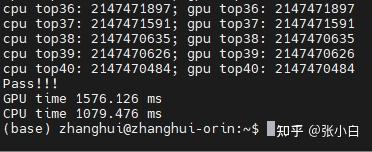
确实比Nano快很多(但是仍然跑不过CPU)
改成top50:

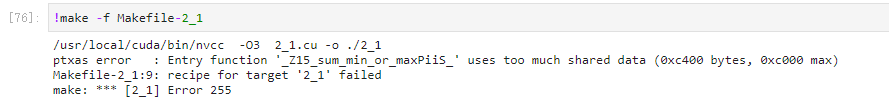
额,还是编译不过去。4G内存和32G内存的设备,看来shared memory是一样大的??
张小白默默看了下定义:
__shared__ int topk_per_block[BLOCK_SIZE * TOPK];当然是的。一个block最多能用48kB。也就是说,如果BLOCK_SIZE设置成前面代码中的256的话,那么TOPK为50的时候,256X50X4已经超过48K了。(1个int占用4个字节)。所以樊老师说了,BLOCK_SIZE=256的时候,TOPK最大能到48。
我们试试:
#define BLOCK_SIZE 256
#define BLOCKS ((N + BLOCK_SIZE - 1) / BLOCK_SIZE)
#define TOPK 48Nano的表现:

改成TOP49,果然不可以编译:
那只有一种办法了,就是降低BLOCK_SIZE,比如说改为128。根据前面的算法,128X4X96等于48K。以此类推,可以算到64,32时候的TOPN最大数量。
我们也就不一一截图了,直接用表格填入结果:
只贴一个:

表格如下:
| TOPN | BLOCK_SIZE | Nano CPU(ms) | NanoGPU(ms) | Orin CPU(ms) | Orin GPU(ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 256 | 433.401 | 252.809 | 131.366 | 44.420 |
| 10 | 256 | 107.692 | 777.333 | 240.604 | 99.995 |
| 20 | 256 | 476.221 | 3414.480 | 511.257 | 256.927 |
| 40 | 256 | 765.036 | 29736.022 | 1079.476 | 1576.126 |
| 48 | 256 | 845.735 | 40406.832 | 1259.630 | 224.732 |
| 50 | 256 | 编译错 | 编译错 | ||
| 50 | 128 | 882.799 | 34380.985 | 1355.741 | 1512.643 |
| 100 | 64 | 1575.113 | 94527.526 | 2709.505 | 1940.573 |
| 96 | 128 | 1513 | 138183.392 | 2576.214 | 5307.144 |
| 97 | 128 | 编译错 | 编译错 | ||
| 192 | 64 | 2831.961 | 653679.935 | 5193.001 | 6091.511 |
| 193 | 64 | 编译错 | 编译错 | ||
| 384 | 32 | 太长不算了 | 太长不算了 | 70072.332 | 10363.466 |
| 385 | 32 | 编译错 | 编译错 | ||
| 48 | 128 | 859.618 | 32778.153 | 1293.652 | 1194.083 |
| 48 | 64 | 853.534 | 21058.578 | 1293.964 | 926.699 |
| 48 | 32 | 845.070 | 15701.802 | 1292.892 | 997.095 |
注:上述结果仅为一次测量结果。不排除多次测量会出现抖动或者差异很大的情况。
以上的结果确认了几个事情:
1.共享内存最大确实只有48K,多一毛都没有。想挤牙膏很难。
2.目前的这种reduce算法还是存在很大的局限性的,它在TOPN较小的时候较为高效。
3.对于TOPN较大,还不如直接调用cublas或者thrust做完全排序(不过这个张小白因为不考试——所以没好好学。。LOL。。下次补上)
4.减小BLOCKSIZE确实可以计算,但是BLOCKSIZE越小,SN占有率就越小。一个SM最多可以驻留2048(或者少一点)的线程,在BLOCKSIZE=128时,占有率为 6.25%;BLOCKSIZE=64时,占有率为 3.125%;BLOCKSIZE=32时,占有率为 1.5625%。从上面的结果也可以看出,BLOCKSIZE变化确实会引起性能较大的变化。
如TOP48:
Orin从BLOCK 256-》128-》64》32分别是 224ms-》1194ms-》926ms-》997ms。后面几个差距不大(因为存在预热),但是256到128发生巨变,说明最佳值在256这里。
Nano从BLOCK 256-》128-》64》32分别是40s-》32s-》32s-》15s。反而是BLOCK越小速度越快。当然这个并不能说明有这个正比关系。只能说明Nano设备并不是运行TOP48的最佳机选。
所以,下次考试,如果可以换成Orin集群。。那大家考试将会多爽啊~~~
在最终开发CUDA程序的时候,是从整个程序的角度发力,如果一个地方并不是关键的,那没有必要优化到极致。用什么算法都可以。先应该花力气解决最关键的部分。
注:往TOPK个元素中插入TOPK个元素,并最终保留TOPK个元素(就是只留下TOPK个元素),如果使用插入法,时间复杂度为O(n^2)的。随着K的扩大,比如从10个变成100个的情况下,算法时间的变大将是灾难性的。这点其实在张小白的测试中也可以略微看出。
其实有训练营的童鞋提出了线性的解决方案,比如双指针法,又比如bucket法,可以将两组TOPK个元素组合成1组按高低排序的K个元素,这个时候的算法时间复杂度是O(n)。另外,针对随机数本身的分布特性,还可以快速求出TOPK。这点,张小白只好留做一个问题,将来再研究了。。。
(未完待续)
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)