Flutter × OpenHarmony 跨端开发:变量与数据结构实战解析
Flutter × OpenHarmony 跨端开发:变量与数据结构实战解析
前言
在现代应用开发中,跨端开发已经成为趋势。Flutter 与 OpenHarmony 的结合,为开发者提供了统一的代码基础,实现多平台部署的可能。本文将以博客应用为例,深入探讨在跨端开发中如何使用 变量与数据结构,并结合实际代码进行详细解析。无论你是 Flutter 新手,还是 OpenHarmony 爱好者,都能从中获得实用经验。
背景
随着多设备生态的丰富,开发者面临以下挑战:
- 代码复用困难:不同平台通常需要不同实现。
- 状态管理复杂:数据状态在不同组件间同步困难。
- 数据结构设计不合理:会导致性能瓶颈与维护困难。
因此,合理使用变量和数据结构,在跨端应用中显得尤为重要。Flutter × OpenHarmony 的组合不仅可以共享 UI 逻辑,还能统一管理数据结构和业务状态。
Flutter × OpenHarmony 跨端开发介绍
Flutter 是 Google 推出的跨端 UI 框架,通过 Dart 语言实现统一 UI 组件和逻辑;OpenHarmony 是华为推出的开源操作系统,支持多设备多终端。结合 Flutter 和 OpenHarmony,可以:
- 共享核心业务逻辑
- 使用统一的数据模型
- 在不同终端快速部署应用
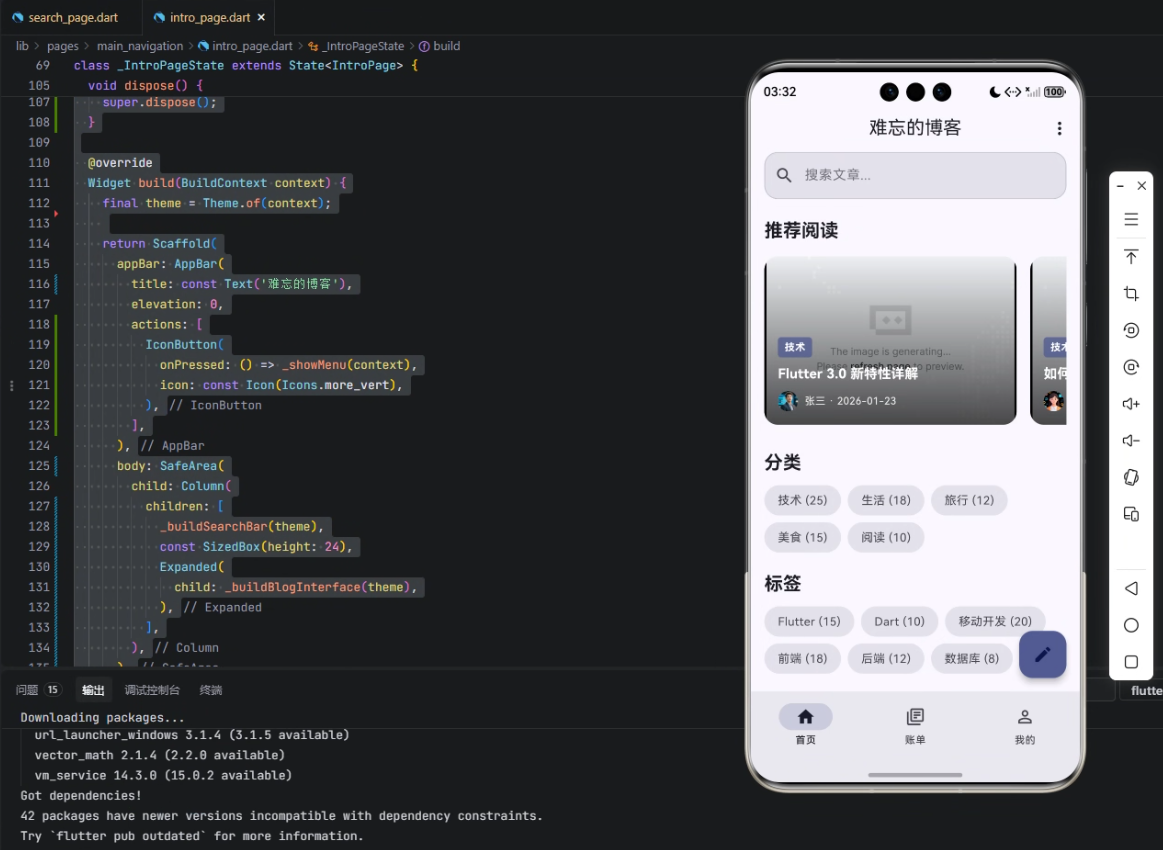
在本文示例中,我们将实现一个博客首页,涉及博客分类、标签和文章的展示,通过变量与数据结构来管理状态和数据。
开发核心代码(详细解析)
下面展示核心实现,并逐行解析:
1. 页面和状态定义
class IntroPage extends StatefulWidget {
const IntroPage({super.key});
@override
State<IntroPage> createState() => _IntroPageState();
}
解析:
- 使用
StatefulWidget是因为博客首页涉及状态变化(如搜索关键字、文章筛选)。 _IntroPageState存放实际状态和逻辑。
2. 数据模型设计
/// 博客分类模型
class BlogCategory {
final String id;
final String name;
final int postCount;
BlogCategory({
required this.id,
required this.name,
required this.postCount,
});
}
/// 博客标签模型
class BlogTag {
final String id;
final String name;
final int postCount;
BlogTag({
required this.id,
required this.name,
required this.postCount,
});
}
/// 博客文章模型
class BlogPost {
final String id;
final String title;
final String excerpt;
final String featuredImage;
final String author;
final String authorAvatar;
final DateTime publishDate;
final int readTime;
final int commentCount;
final List<BlogCategory> categories;
final List<BlogTag> tags;
final int views;
BlogPost({
required this.id,
required this.title,
required this.excerpt,
required this.featuredImage,
required this.author,
required this.authorAvatar,
required this.publishDate,
required this.readTime,
required this.commentCount,
required this.categories,
required this.tags,
required this.views,
});
}
解析:
- 每种数据类型都用 类(class) 来封装,方便跨组件共享。
BlogPost内部包含列表类型categories和tags,体现组合关系,方便对文章进行多维度管理。- 使用
final确保数据不可变,提高稳定性和安全性。
3. 状态变量和初始化
class _IntroPageState extends State<IntroPage> {
BlogCategory? _selectedCategory;
BlogTag? _selectedTag;
String _searchKeyword = '';
final TextEditingController _searchController = TextEditingController();
List<BlogPost> _posts = [];
List<BlogCategory> _categories = [];
List<BlogTag> _tags = [];
List<BlogPost> _featuredPosts = [];
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_categories = _getSampleCategories();
_tags = _getSampleTags();
_posts = _getSamplePosts();
_featuredPosts = _getSampleFeaturedPosts();
}
@override
void dispose() {
_searchController.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
解析:
_selectedCategory和_selectedTag:当前用户选中的分类或标签。_searchKeyword:搜索框输入值。_searchController:控制搜索输入框文本。_posts、_categories、_tags、_featuredPosts:存放不同类型的博客数据。initState()初始化示例数据,用于开发和测试。
4. UI 构建与数据绑定
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final theme = Theme.of(context);
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('难忘的博客'),
elevation: 0,
actions: [
IconButton(
onPressed: () => _showMenu(context),
icon: const Icon(Icons.more_vert),
),
],
),
body: SafeArea(
child: Column(
children: [
_buildSearchBar(theme),
const SizedBox(height: 24),
Expanded(
child: _buildBlogInterface(theme),
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: _buildFloatingActionButton(theme),
);
}
}
解析:
AppBar:顶部导航栏,显示博客名称和更多操作按钮。_buildSearchBar(theme):搜索框,绑定_searchController和_searchKeyword。_buildBlogInterface(theme):博客文章、分类和标签列表展示区域。floatingActionButton:浮动按钮,可用于添加文章或其他操作。
通过数据模型和状态变量,UI 与业务数据实现了响应式绑定,在跨端场景下可保持一致。
心得
- 数据模型设计优先:合理的数据结构能极大提高跨组件和跨平台的数据复用性。
- 状态管理要清晰:尤其是跨端开发,状态混乱会导致不同平台显示不一致。
- 代码可读性重要:Flutter 的声明式 UI + OpenHarmony 的多终端适配,要求变量命名和数据结构清晰明了。

总结
本文通过 Flutter × OpenHarmony 的跨端开发示例,详细解析了博客应用的 变量与数据结构设计。我们学习了如何用类封装数据、使用状态变量管理 UI,以及在跨端环境下保持数据一致性。合理的变量设计和数据结构不仅能提高开发效率,还能让应用在多端表现稳定一致。对于任何希望从单端扩展到多端的开发者来说,这是一个非常实用的参考案例。
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)