Spring AOP初步理解及使用
Spring AOP
一、简介
面向切面编程(Aspect-oriented Programming,俗称AOP)提供了一种面向对象编程(Object-oriented Programming,俗称OOP)的补充,面向对象编程最核心的单元是类(class),然而面向切面编程最核心的单元是切面(Aspects)。与面向对象的顺序流程不同,AOP采用的是横向切面的方式,注入与主业务流程无关的功能,例如事务管理和日志管理。
Spring的一个关键组件是AOP框架。 虽然Spring IoC容器不依赖于AOP(意味着你不需要在IOC中依赖AOP),但AOP为Spring IoC提供了非常强大的中间件解决方案。
二、概念
在深入学习SpringAOP 之前,让我们先对AOP的几个基本术语有个大致的概念,这些概念不是很容易理解,比较抽象,可以知道有这么几个概念,下面一起来看一下:
切面(Aspect): Aspect 声明类似于 Java 中的类声明,事务管理是AOP一个最典型的应用。在AOP中,切面一般使用@Aspect注解来使用,在XML 中,可以使用<aop:aspect>来定义一个切面。连接点(Join Point): 一个在程序执行期间的某一个操作,就像是执行一个方法或者处理一个异常。在Spring AOP中,一个连接点就代表了一个方法的执行。通知(Advice):在切面中(类)的某个连接点(方法出)采取的动作,会有四种不同的通知方式: around(环绕通知),before(前置通知),after(后置通知), exception(异常通知),return(返回通知)。许多AOP框架(包括Spring)将建议把通知作为为拦截器,并在连接点周围维护一系列拦截器。切入点(Pointcut):表示一组连接点,通知与切入点表达式有关,并在切入点匹配的任何连接点处运行(例如执行具有特定名称的方法)。由切入点表达式匹配的连接点的概念是AOP的核心,Spring默认使用AspectJ切入点表达式语言。介绍(Introduction):introduction可以为原有的对象增加新的属性和方法。例如,你可以使用introduction使bean实现IsModified接口,以简化缓存。目标对象(Target Object):由一个或者多个切面代理的对象。也被称为"切面对象"。由于Spring AOP是使用运行时代理实现的,因此该对象始终是代理对象。AOP代理(AOP proxy):由AOP框架创建的对象,在Spring框架中,AOP代理对象有两种:JDK动态代理和CGLIB代理织入(Weaving):是指把增强应用到目标对象来创建新的代理对象的过程,它(例如 AspectJ 编译器)可以在编译时期,加载时期或者运行时期完成。与其他纯Java AOP框架一样,Spring AOP在运行时进行织入。
1 Spring AOP 中通知的分类
- 前置通知(Before Advice): 在目标方法被调用前调用通知功能;相关的类
org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice - 后置通知(After Advice): 在目标方法被调用之后调用通知功能;相关的类
org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice - 返回通知(After-returning): 在目标方法成功执行之后调用通知功能;
- 异常通知(After-throwing): 在目标方法抛出异常之后调用通知功能;相关的类
org.springframework.aop.ThrowsAdvice - 环绕通知(Around): 把整个目标方法包裹起来,在被调用前和调用之后分别调用通知功能相关的类
org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor
2 Spring AOP 中织入的三种时期
编译期:切面在目标类编译时被织入,这种方式需要特殊的编译器。AspectJ 的织入编译器就是以这种方式织入切面的。类加载期:切面在目标类加载到 JVM 时被织入,这种方式需要特殊的类加载器( ClassLoader ),它可以在目标类引入应用之前增强目标类的字节码。运行期:切面在应用运行的某个时期被织入。一般情况下,在织入切面时,AOP容器会为目标对象动态创建一个代理对象,Spring AOP 采用的就是这种织入方式。
三、实现方式
AOP 采用了两种实现方式:静态织入(AspectJ 实现)和动态代理(Spring AOP实现)
1 AspectJ
AspectJ 是一个采用Java 实现的AOP框架,它能够对代码进行编译(一般在编译期进行),让代码具有AspectJ 的 AOP 功能,AspectJ 是目前实现 AOP 框架中最成熟,功能最丰富的语言。ApectJ 主要采用的是编译期静态织入的方式。在这个期间使用 AspectJ 的 acj 编译器(类似 javac)把 aspect 类编译成 class 字节码后,在 java 目标类编译时织入,即先编译 aspect 类再编译目标类。
2 Spring AOP 实现
Spring AOP 是通过动态代理技术实现的,而动态代理是基于反射设计的。Spring AOP 采用了两种混合的实现方式:JDK 动态代理和 CGLib 动态代理,分别来理解一下
3 总结
- JDK动态代理:Spring AOP的首选方法。 每当目标对象实现一个接口时,就会使用JDK动态代理。目标对象必须实现接口
- CGLIB代理:如果目标对象没有实现接口,则可以使用CGLIB代理。
四、Spring对AOP的支持
Spring 提供了两种AOP 的实现:基于注解式配置和基于XML配置
1 @AspectJ 支持
为了在Spring 配置中使用@AspectJ ,你需要启用Spring支持,以根据@AspectJ切面配置Spring AOP,并配置自动代理。自动代理意味着,Spring 会根据自动代理为 Bean 生成代理来拦截方法的调用,并确保根据需要执行拦截。
可以使用XML或Java样式配置启用@AspectJ支持。 在任何一种情况下,都还需要确保AspectJ的aspectjweaver.jar 第三方库位于应用程序的类路径中(版本1.8或更高版本)。
2 开启@AspectJ 支持
使用@Configuration 支持@AspectJ 的时候,需要添加 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 注解,就像下面例子展示的这样来开启 AOP代理
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AppConfig {}
也可以使用XML配置来开启@AspectJ 支持
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
默认你已经添加了 aop 的schema 空间,如果没有的话,你需要手动添加
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- bean definitions here -->
</beans>
(1)声明一个切面
在启用了@AspectJ支持的情况下,在应用程序上下文中定义的任何bean都具有@AspectJ方面的类(具有@Aspect注释),Spring会自动检测并用于配置Spring AOP。
使用XML 配置的方式定义一个切面
<aop:aspect />
使用注解的方式定义一个切面
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {}
切面(也就是用@Aspect注解的类)就像其他类一样有属性和方法。它们能够包含切入点,通知和介绍声明。
通过自动扫描检测切面
你可以在Spring XML 配置中将切面类注册为常规的bean,或者通过类路径扫描自动检测它们 - 与任何其他Spring管理的bean相同。然而,只是注解了@Aspect 的类不会被当作bean 进行管理,你还需要在类上面添加 @Component 注解,把它当作一个组件交给 Spring 管理。
(2)定义一个切点
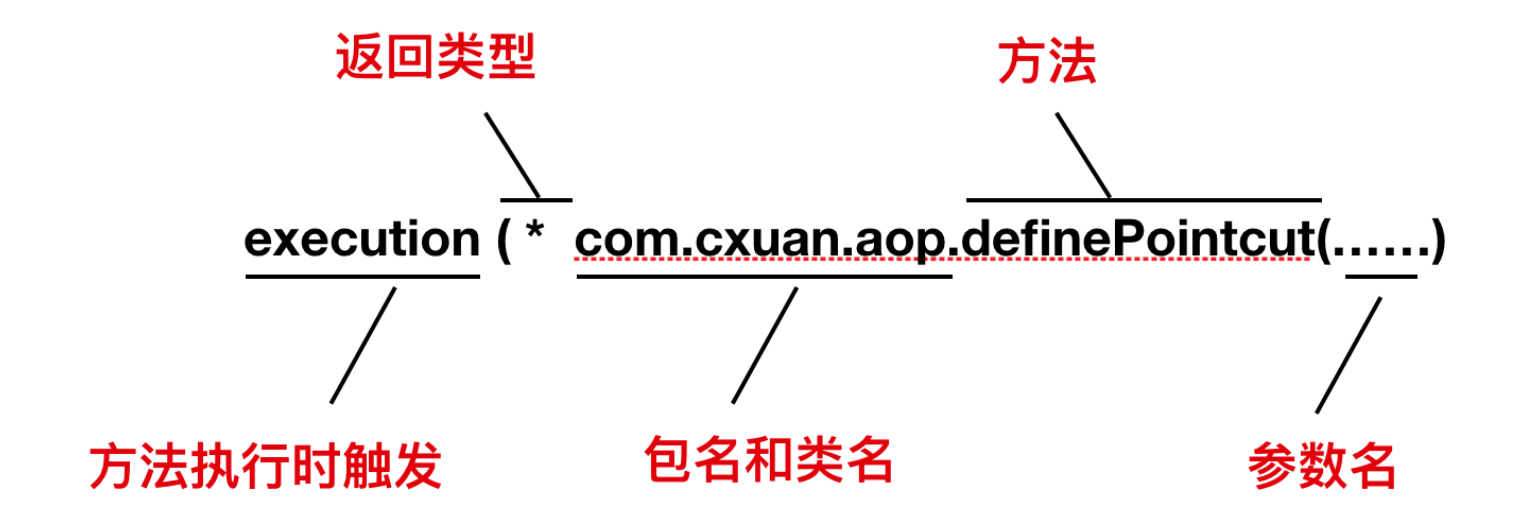
一个切点由两部分组成:包含名称和任何参数以及切入点表达式的签名,该表达式能够确定我们想要执行的方法。在@AspectJ注释风格的AOP中,切入点表达式需要用@Pointcut注解标注(这个表达式作为方法的签名,它的返回值必须是 void)。
@Pointcut("execution(* transfer(..))") // 切入点表达式
private void definePointcut() {}// 方法签名
切入点表达式的编写规则如下:
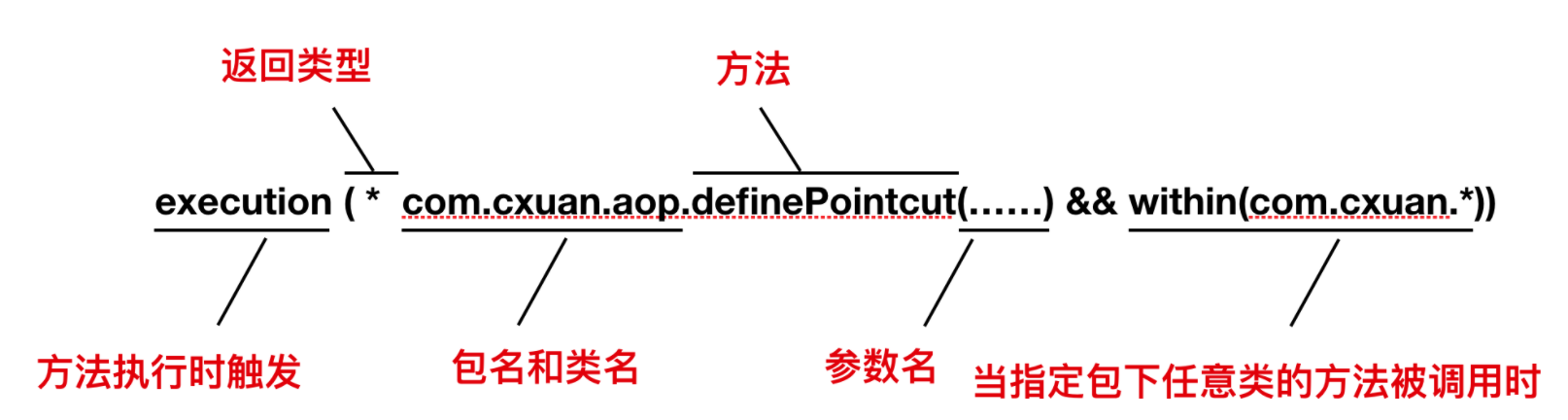
现在假设我们需要配置的切点仅仅匹配指定的包,就可以使用 within() 限定符来表示,如下表达式所述:
请注意我们使用了 && 操作符把 execution() 和 within() 指示器连接在一起,表示的是 和 的关系,类似的,你还可以使用 || 操作来表示 或 的关系, 使用 ! 表示 非 的关系。
除了within() 表示的限定符外,还有其它的限定符,下面是一个限定符表
| AspectJ 描述符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| arg() | 限制连接点匹配参数为指定类型的执行方法 |
| @args() | 限制连接点匹配参数由指定注解标注的执行方法 |
| execution() | 用于匹配是连接点的执行方法 |
| this() | 限制连接点匹配的AOP代理的bean引用为指定类型的类 |
| target | 限制连接点匹配目标对象为指定类型的类 |
| @target() | 限制连接点匹配特定的执行对象,这些对象对应的类要具有指定类型的注解 |
| within() | 限制连接点匹配指定的类型 |
| @within() | 限制连接点匹配指定注解所标注的类型 |
| @annotationn | 限定匹配带有指定注解的连接点 |
使用XML配置来配置切点
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref = "">
<aop:poincut id = "" expression="execution(** com.cxuan.aop.definePointcut(......))"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
(3)声明一个通知
上面的例子就很清晰了,定义了一个 Audience 切面,并在切面中定义了一个performance() 的切点,下面各自定义了表演之前、表演之后返回、表演失败的时候进行通知,除此之外,你还需要在main 方法中开启 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 来开启自动代理。
除了使用Java Config 的方式外,你还可以使用基于XML的配置方式
<bean id="logException" class="org.lanqiao.aop.LogException"></bean>
<aop:config>
<!-- 切入点(连接线的一端:业务类的具体方法) -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(public * org.lanqiao.service.impl.StudentServiceImpl.addStudent(..))" id="poioncut3"/>
<!-- (连接线的另一端:通知 类) -->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="logException" pointcut-ref="poioncut3" />
</aop:config>
当然,这种切点定义的比较冗余,为了解决这种类似 if...else... 灾难性的业务逻辑,你需要单独定义一个<aop:pointcut>,然后使用 pointcut-ref 属性指向上面那个标签,就像下面这样
(4)环绕通知
在目标方法执行之前和之后都可以执行额外代码的通知。在环绕通知中必须显式的调用目标方法,目标方法才会执行,这个显式调用时通过ProceedingJoinPoint来实现的,可以在环绕通知中接收一个此类型的形参,spring容器会自动将该对象传入,注意这个参数必须处在环绕通知的第一个形参位置。
环绕通知需要返回返回值,否则真正调用者将拿不到返回值,只能得到一个null。下面是环绕通知的一个示例
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pc1"/>
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("1 -- around before...");
Object obj = jp.proceed(); //--显式的调用目标方法
System.out.println("1 -- around after...");
return obj;
}

五、AOP实战(注解版)
1 简介
StudentService类具有SayHello()方法表示说Hello,但是在学生和别人说”Hello“之前,必须张开嘴巴和睁开眼睛,说完“Hello”之后再来一个回眸微笑,图示如下:

2 实现方式一
(1)pom依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.0.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
(2)Service接口和实现类
## 接口:
package org.ymx.service;
public interface StudentService {
void sayHello();
}
## 实现类:
package org.ymx.service.impl;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.ymx.service.StudentService;
@Service
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Override
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}
(3)切面类
package org.ymx.service;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 注解@Aspect标识该类为切面类
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class ServiceAspect {
/**
* 通过注解@Pointcut定义切点,stuSayHello()只是一个标识,无所谓是什么,
* 方法中内容本身也是空的,使用该切点的地方直接通过标识stuSayHello()引用切点表达式。
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* org.ymx.service.impl.StudentServiceImpl.sayHello(..))")
public void stuSayHello() {
}
/**
* 说话之前--张开嘴巴
*/
@Before("stuSayHello()")
public void openMouth() {
System.out.println("Opens his mouth");
}
/**
* 说话之前--睁开眼睛
*/
@Before("stuSayHello()")
public void openEyes() {
System.out.println("Open one's eyes");
}
/**
* 说话之后--微笑
*/
@After("stuSayHello()")
public void smile() {
System.out.println("Smile");
}
}

(4)AOP全局配置
package org.ymx.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
/**
* Jdk代理:基于接口的代理,一定是基于接口,会生成目标对象的接口的子对象。
* Cglib代理:基于类的代理,不需要基于接口,会生成目标对象的子对象。
*
* 1. 注解@EnableAspectJAutoProxy开启代理;
*
* 2. 如果属性proxyTargetClass默认为false, 表示使用jdk动态代理织入增强;
*
* 3. 如果属性proxyTargetClass设置为true,表示使用Cglib动态代理技术织入增强;
*
* 4. 如果属性proxyTargetClass设置为false,但是目标类没有声明接口,
* Spring aop还是会使用Cglib动态代理,也就是说非接口的类要生成代理都用Cglib。
*/
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
@ComponentScan("org.ymx.service")
public class AopConfig {
}
(5)测试
package test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import org.ymx.config.AopConfig;
import org.ymx.service.StudentService;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = AopConfig.class) //加载全局配置
public class test01 {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@Test
public void Test01(){
studentService.sayHello();
}
}
测试时一定要加载全局配置@ContextConfiguration(classes = AopConfig.class)不然AOP不起作用
3 实现方式二
与上述方式实现唯一不同点在于切面类使用的 @Around注解来替代@Before和@After
package org.ymx.service;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 注解@Aspect标识该类为切面类
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class ServiceAspect {
/**
* 通过注解@Pointcut定义切点,stuSayHello()只是一个标识,无所谓是什么,
* 方法中内容本身也是空的,使用该切点的地方直接通过标识stuSayHello()引用切点表达式。
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* org.ymx.service.impl.StudentServiceImpl.sayHello(..))")
public void stuSayHello() {
}
@Around("stuSayHello()")
public void testAround(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) {
try {
System.out.println("Opens his mouth");
System.out.println("Open one's eyes");
jp.proceed();//执行方法
System.out.println("Smile");
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("没说出来");
}
}
}
4 测试结果

文章内容部分引自:
https://blog.csdn.net/yhl_jxy/article/details/78815636
https://github.com/crisxuan/bestJavaer
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)