Java基础 第一节 第十九课
数组越界异常
观察一下代码, 运行后会出现什么结果.
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
System.out.println(arr[3]);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
创建数组, 赋值 3 个元素, 数组的索引就是 0, 1, 2. 没有 3 索引, 因此我们不能访问数组中不存在的索引. 程序运行后会抛出ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException数组越界异常. 在开发中, 数组越界异常是不能出现的, 一旦出现了, 就必须要修改我们编写的代码.

数组空指针异常
观察一下代码, 运行后会出现什么结果.
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
arr = null;
System.out.println(arr[0]);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
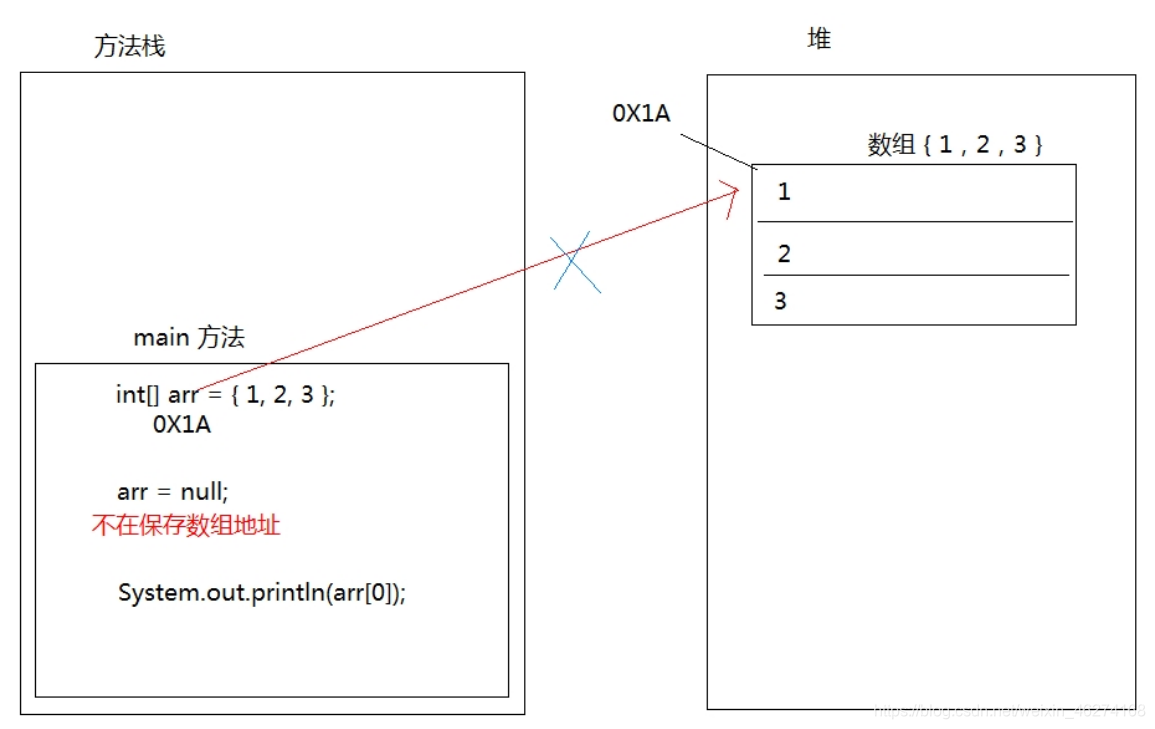
arr = null 这行代码, 意味着变量 arr 将不会在保存数组的内存地址, 也就不允许再操作数组了. 因此运行的时候会NullPointerException空指针异常. 在开发中, 数组的空指针异常是不能出现的. 一旦出现了, 就必须要修改我们编写的代码.

空指针异常在内存图中的表现
数组的遍历
数组的遍历: 就是将数组中的每个元素分别获取出来, 就是遍历. 遍历也是数组操作中的基石.
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
System.out.println(arr[0]);
System.out.println(arr[1]);
System.out.println(arr[2]);
System.out.println(arr[3]);
System.out.println(arr[4]);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
以上代码是可以将数组中每个元素遍历出来, 但是如果数组元素非常多. 这种写法肯定不行, 因此我们需要改造成循环的写法. 数组的索引 0 到 length-1, 可以作为循环的条件出现.
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
数组获取最大值元素
最大值获取: 从数组的所有元素中找出最大值.
实现思路:
- 定义变量, 保存数组 0 索引上的元素
- 遍历数组, 获取出数组中的每个元素
- 将遍历到的元素和保存数组 0 索引上值的变量进行比较
- 如果数组元素的值大于了变量的值, 变量记录住新的值
- 数组循环遍历结果, 变量保存的就是数组中的最大值
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 5, 15, 2000, 10000, 100, 4000 };
// 定义变量,保存数组中0索引的元素
int max = arr[0];
// 遍历数组,取出每个元素
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// 遍历到的元素和变量max比较
// 如果数组元素大于max
if (arr[i] > max) {
// max记录住大值
max = arr[i];
}
}
System.out.println("数组最大值是: " + max);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
数组反转
数组反转: 数组中的元素颠倒顺序, 例如初始数组为 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 反转后数组为 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 .
实现思想:
- 实现反转, 就需要将数组最远端元素位置交换
- 定义两个变量, 保存数组的最小索引和最大索引
- 两个索引上的元素交换位置
- 最小索引++, 最大索引–, 再次交换位置
- 最小索引超过了最大索引, 数组反转操作结束
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
/*
循环中定义变量min=0最小索引
max=arr.length‐1最大索引
min++,max‐‐
*/
for (int min = 0, max = arr.length ‐ 1; min <= max; min++, max‐‐) {
// 利用第三方变量完成数组中的元素交换
int temp = arr[min];
arr[min] = arr[max];
arr[max] = temp;
}
// 反转后,遍历数组
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
文章来源: iamarookie.blog.csdn.net,作者:我是小白呀,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:iamarookie.blog.csdn.net/article/details/109968425
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)