【Linux C编程】第七章 系统IO函数2
一、整体大纲
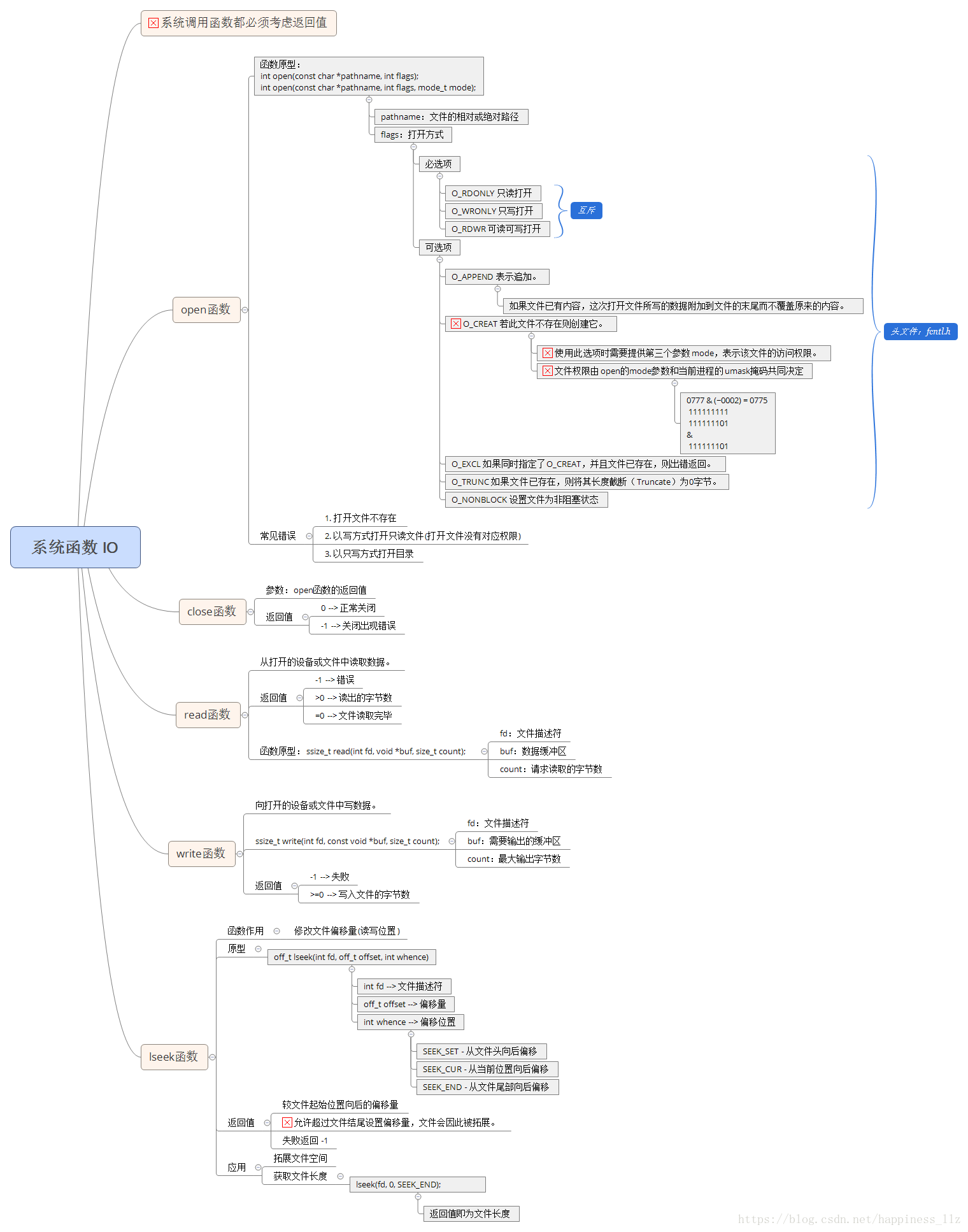
二、 系统IO函数
1. 一些概念
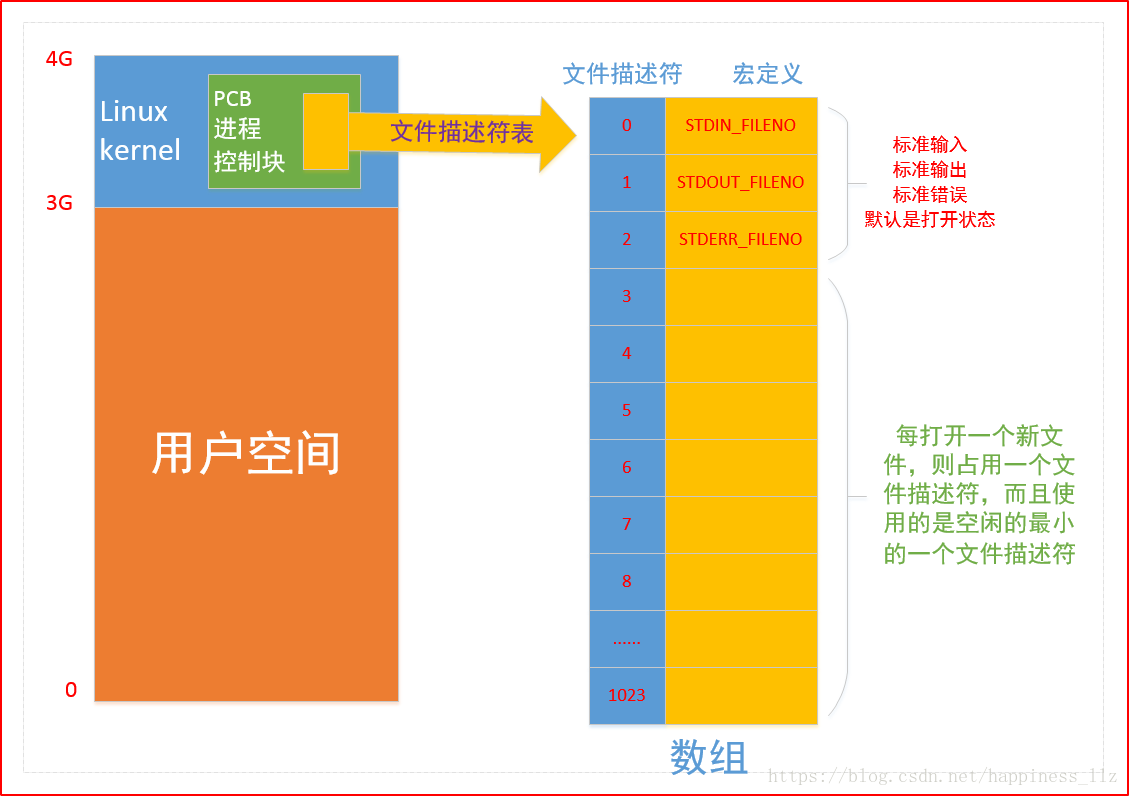
文件描述符
PCB
C库函的IO缓冲区
1) 文件描述符
int 类型
一个进程最多可打开多少文件
2) pcb
进程控制块
在其中有一个文件描述符表 -- 数组[1024]
C库IO函数工作流程:
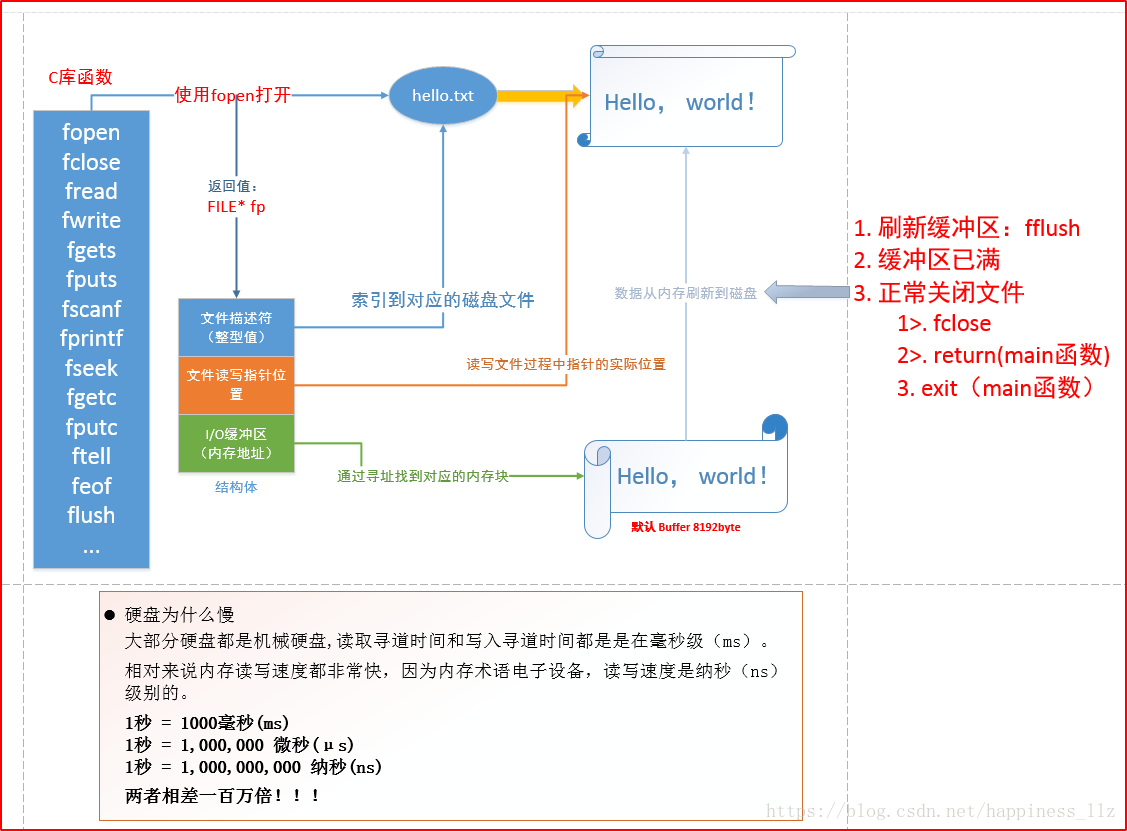
pcb和文件描述符:
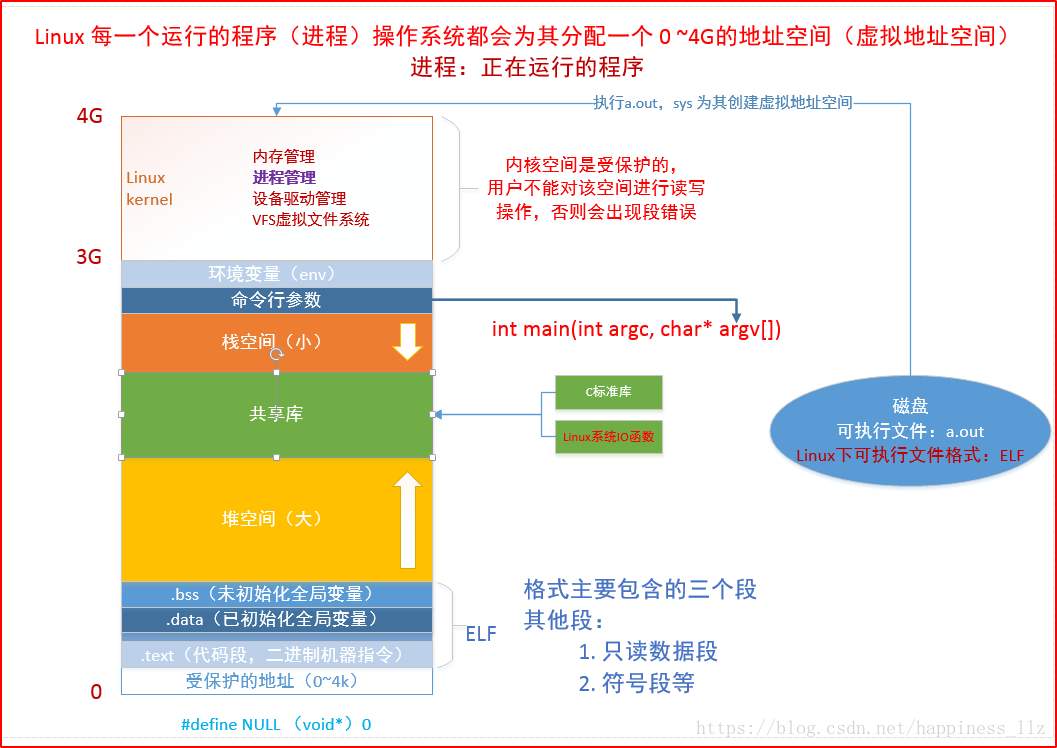
2. 虚拟地址空间
虚拟地址空间就是程序启动起来之后从硬盘上会有一块虚拟内存分配出来。
cpu 为什么要使用虚拟地址空间与物理地址空间映射?解决了什么样的问题?
1)方便编译器和操作系统安排程序的地址分布。
程序可以使用一系列相邻的虚拟地址来访问物理内存中不相邻的大内存缓冲区。通过虚拟地址空间与物理地址空间映射解决不连续的缓冲区的问题。
2)方便进程之间隔离
不同进程使用的虚拟地址彼此隔离。一个进程中的代码无法更改正在由另一进程使用的物理内存。
3)方便OS使用你那可怜的内存。
程序可以使用一系列虚拟地址来访问大于可用物理内存的内存缓冲区。当物理内存的供应量变小时,
内存管理器会将物理内存页(通常大小为 4 KB)保存到磁盘文件。数据或代码页会根据需要在物理内存与磁盘之间移动。
虚拟地址空间的布局如下:
0-3G是用户空间 3-4G是内核空间
用户区 内核区
代码段
已经初始化的全局变量
未被初始化的全局变量
堆 -- 从下往上
共享库
栈 - 从上往下
环境变量
内核区
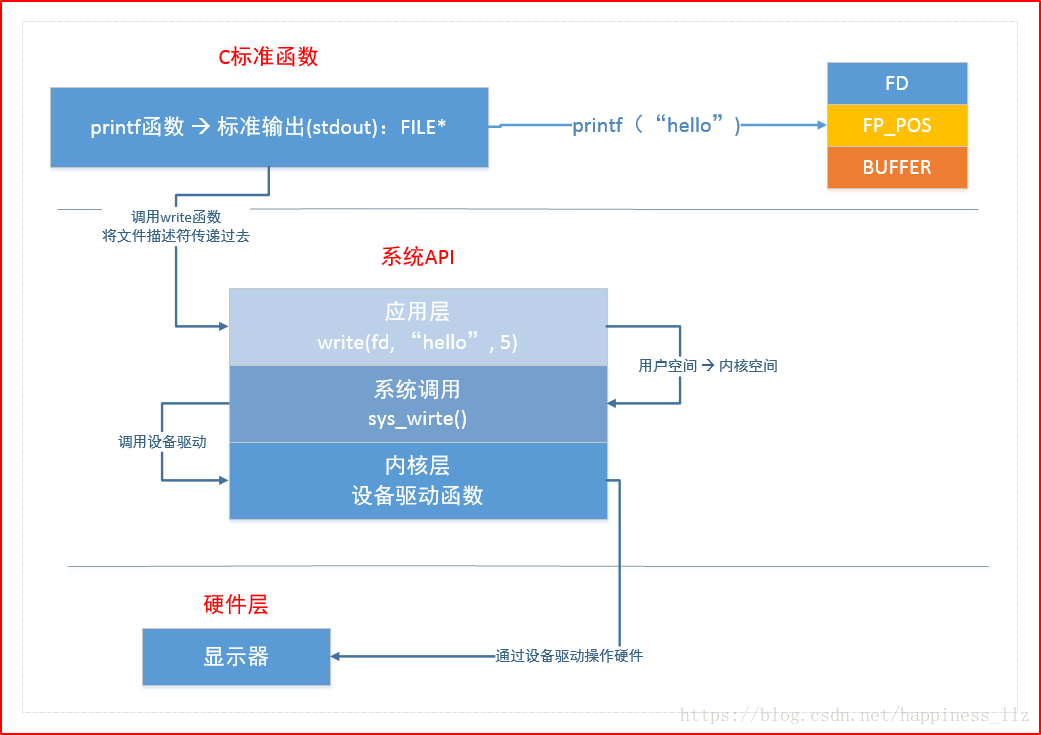
3. C库函数与系统函数的关系
FD:文件描述符 FP_POS:文件指针 BUFFER:缓冲区
write对0-3G的用户空间进行操作 sys_write()对3-4G的内核空间进行操作
4. IO函数介绍
1)open
- 查看 man 2 open
- 头文件:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>- 函数原型:
int open(const char *pathname, int flags);
int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);- 参数说明
pathname 文件名
flags
必选项:
O_RDONLY 只读
O_WRONLY 只写
O_RDWR 读写
可选项:
O_APPEND 追加
O_CREAT 创建文件
O_EXCL和O_CREATE一起使用,如果文件存在则报错
O_NONBLOCK 非阻塞
Mode 权限位,最终(mode&~umask)
- 返回值:
成功:返回最小的可用文件描述符
失败:返回-1,并且设置errno
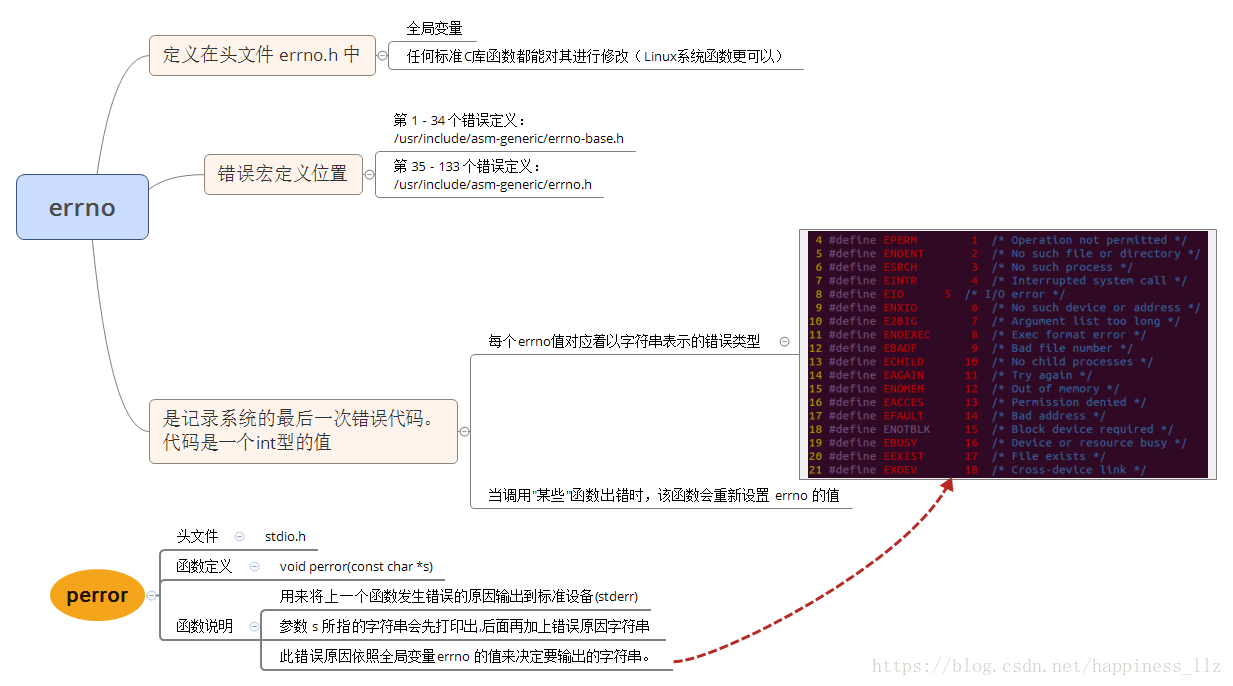
- open函数中的errno:
使用open实现一个touch功能
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<fcntl.h>
3 #include<sys/types.h>
4 #include<sys/stat.h>
5 #include<unistd.h>
6
7 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
8 {
9 if (argc != 2)
10 {
11 printf("./a.out filename\n")
12 return -1
13 }
14 int fd = open(argv[1], O_CREAT|O_TRUNC|O_WRONLY, 0666);
15 close(fd);
16
17 return 0;
18 }
一个进程打开的最大文件数(1024)
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<unistd.h>
3 #include<sys/types.h>
4 #include<sys/stat.h>
5 #include<fcntl.h>
6 #include<strings.h>
7
8 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
9 {
10 int num = 3;
11 char filename[128] = {0};
12 while(1)
13 {
14 sprintf(filename, "temp_%04d", num++);
15 if (open(filename, O_RDONLY|O_CREAT, 0666) < 0)
16 {
17 perror("open err:");
18 break;
19 }
20 }
21 printf("num == %d\n", num);
22
23 return 0;
24 }
2)close
- 作用:关闭文件描述符
- 头文件:
#include <unistd.h>- 函数原型:
int close(int fd);- 参数说明:
fd文件描述符
- 返回值:
成功:返回0
失败:返回-1,并且设置errno
3)read读
- 头文件
#include <unistd.h>- 函数原型
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);- 参数说明
fd 文件描述符
buf缓冲区
count缓冲区大小
- 返回值
失败:返回-1,设置errno
成功:返回读到的字节数
0代表读到文件末尾
非阻塞的情况下read返回-1,但是此时需要判断error的值。
4)write写
- 头文件
#include <unistd.h>- 函数原型
ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);- 参数说明:
fd文件描述符
buf缓冲区
count缓冲区大小
- 返回值
失败:返回-1,设置errno
成功:返回写入的字节数
0代表未写入
实现一个cat功能
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<fcntl.h>
3 #include<sys/types.h>
4 #include<sys/stat.h>
5 #include<unistd.h>
6
7 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
8 {
9 if (argc != 2)
10 {
11 printf("./a.out filename\n")
12 return -1
13 }
14 int fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
15 char buf[256] = {0};
16 int ret = 0;
17 while ((ret = read(fd, buf, ziseof(buf))) != 0)
18 {
19 if (ret == -1)
20 {
21 perror("read err:");
22 return -1;
23 }
24 else
25 {
26 write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, ret);
27 }
28 }
29
30 close(fd);
31
32 return 0;
33 }
需求:给一个文件中写入内容,写完之后打开该文件再读取写入的内容?
bug版本
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<fcntl.h>
3 #include<sys/types.h>
4 #include<sys/stat.h>
5 #include<unistd.h>
6
7 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
8 {
9 if (argc != 2)
10 {
11 printf("./a.out filename\n");
12 return -1;
13 }
14 int fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR|O_CREAT, 0666);
15
16 char data[12] = "hello world";
17 write(fd, data, sizeof(data));
18
19 char buf[256] = {0};
20 int ret = 0;
21 while ((ret = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf))) != 0)
22 {
23 if (ret == -1)
24 {
25 perror("read err:");
26 return -1;
27 }
28 else
29 {
30 write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, ret); //STDIN_FILENO, STDERR_FILENO
31 }
32 }
33
34 close(fd);
35
36 return 0;
37 }
结果:内容写入到文件中,但是并未按预期输出到屏幕上。
原因:是由于write完成之后,fd到了文件末尾,因此read时到了文件末尾,无法读取文件数据
解决方法:写完之后将文件指针设置到文件开头,使用请看下文要介绍的lseek函数。
5)lseek写
- 头文件
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>- 函数原型
off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence);- 参数说明
fd文件描述符
offset偏移量
whence:
SEEK_SET 文件开始位置
SEEK_CUR 文件当前位置
SEEK_END 文件结尾
- 返回值
失败:返回-1,设置errno
成功:返回当前位置到文件开头的长度
- lseek作用
移动文件读写位置
计算文件大小
拓展文件
示例:
a. 移动文件读写位置
修改上例的bug(写入文件内容并读取文件内容打印到屏幕)
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<fcntl.h>
3 #include<sys/types.h>
4 #include<sys/stat.h>
5 #include<unistd.h>
6
7 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
8 {
9 if (argc != 2)
10 {
11 printf("./a.out filename\n");
12 return -1;
13 }
14 int fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR|O_CREAT, 0666);
15
16 char data[12] = "hello world";
17 write(fd, data, sizeof(data));
18 //文件读写位置此时在末尾
19 //需要移动读写位置
20 lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET); //将fd移动到文件头
21
22 char buf[256] = {0};
23 int ret = 0;
24 while ((ret = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf))) != 0)
25 {
26 if (ret == -1)
27 {
28 perror("read err:");
29 return -1;
30 }
31 else
32 {
33 write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, ret); //STDIN_FILENO, STDERR_FILENO
34 }
35 }
36
37 close(fd);
38
39 return 0;
40 }
b. 计算文件大小
计算文件大小(输出文件字节数)
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<fcntl.h>
3 #include<sys/types.h>
4 #include<sys/stat.h>
5 #include<unistd.h>
6
7 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
8 {
9 if (argc != 2)
10 {
11 printf("./a.out filename\n");
12 return -1;
13 }
14 int fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
15
16 int ret = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END); //将fd移动到文件头
17 printf("file size is %d\n", ret); //注意实际读到的文件大小为ret-1
18
19 close(fd);
20
21 return 0;
22 }
c. 拓展文件
拓展文件
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<fcntl.h>
3 #include<sys/types.h>
4 #include<sys/stat.h>
5 #include<unistd.h>
6
7 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
8 {
9 if (argc != 2)
10 {
11 printf("./a.out filename\n");
12 return -1;
13 }
14 int fd = open(argv[1], O_WRONLY|O_CREAT, 0666);
15 //拓展文件
16 int ret = lseek(fd, 1024, SEEK_END); //将fd移动到文件头
17 //需要至少写一次,否则不能保存
18 write(fd, "a", 1);
19 printf("file size is %d\n", ret);
20
21 close(fd);
22
23 return 0;
24 }
阻塞的概念:
read函数在读设备或者读管道,或者读网络的时候。
输入输出设备对应的/dev/tty。
6)fcntl
- 头文件
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>- 函数原型
int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ... /* arg */ );- 参数说明:
fd文件描述符
cmd 命令
- 返回值
不同的cmd返回值不同
使用fcntl函数实现读非阻塞
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<fcntl.h>
3 #include<sys/types.h>
4 #include<sys/stat.h>
5 #include<unistd.h>
6
7 int main(int argc, char *argv[])
8 {
9 //O_NONBLOCK设置为非阻塞
10 int fd = open("/dev/tty", O_RDWR);
11 //fcntl()函数,设置非阻塞
12 int flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL);
13 flags |= O_NONBLOCK;
14 fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, flags);
15
16 char buf[256] = {0};
17 int ret = 0;
18 while(1)
19 {
20 //如果没有设置O_NONBLOCK
21 ret = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
22 if (ret < 0)
23 {
24 perror("read err:");
25 printf("ret is %d\n", ret);
26 }
27
28 if (ret)
29 {
30 printf("buf is %s\n", buf);
31 }
32 printf("haha\n");
33 sleep(1);
34 }
35 close(fd);
36
37 return 0;
38 }
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)